Secure Secrets Management on AWS SAM with AWS Secrets Manager
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, where data security reigns supreme, the management of sensitive information holds the key to a robust and resilient infrastructure. AWS Secrets Manager comes in handy as a crucial guardian of digital assets by providing a secure vault for managing access credentials, API keys, and other critical information on AWS.
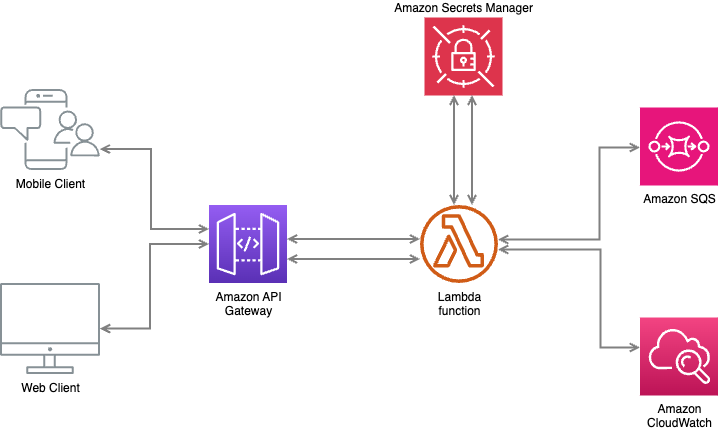
In this blog, we’ll uncover the significance of AWS Secrets Manager, delving into its pivotal role in secure credential management and seamless integration with AWS services such as AWS Lambda, Amazon SQS and Amazon API Gateway. We will build a NodeJS API with AWS SAM where we will send our notes to Amazon SQS as messages after authenticating through basic auth credentials stored in AWS Secrets Manager.
Let’s get started
Prerequisite
- Basic skill in NodeJs
- AWS Account
- AWS CLI
- SAM CLI
Code Repo
# clone the repo from github $ git clone https://github.com/bensonmacharia/secrets-management-sam.git
Environment Setup
# create project directory $ mkdir secrets-management-sam && cd secrets-management-sam # create aws sam config file $ touch template.yaml # create files for our lambda functions logic $ touch src/handlers/auth-token.mjs $ touch src/handlers/add-note.mjs $ touch src/handlers/get-all-notes.mjs # open in vscode IDE $ code .
Edit template.yaml file
The template.yaml serves as the foundational configuration file for our serverless application in AWS SAM. In our SAM application, we will have an API Gateway with API auth key set for all endpoints, an SQS queue to keep our notes, a Secrets Manager to store our basic auth credentials and three lambda functions.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: >-
secrets-management-sam
Transform:
- AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Resources:
# Create an API Gateway with API auth Key
ApiGatewayEndpoint:
Type: "AWS::Serverless::Api"
Properties:
StageName: Prod
Auth:
# Require API Key for all endpoints
ApiKeyRequired: true
UsagePlan:
CreateUsagePlan: PER_API
UsagePlanName: GatewayAuthorization
# A Queue to keep our notes
NotesSQSQueue:
Type: AWS::SQS::Queue
Properties:
QueueName: NotesQueue
VisibilityTimeout: 300
MessageRetentionPeriod: 86400
# A Secret Manager to keep our basic auth secret
AuthTokenSecretManager:
Type: AWS::SecretsManager::Secret
Properties:
Name: AuthTokenSecretManager
Description: "This secret has a dynamically generated secret token."
# Generate a random string 32 charatcers long for api Basic authentication
GenerateSecretString:
GenerateStringKey: "authtoken"
PasswordLength: 32
ExcludeCharacters: '"@/\:;+*'''
SecretStringTemplate: '{"username": "samuser"}'
# This is a Lambda function config associated with the source code: auth-token.js for fetching the secret from secrets manager and creating an auth token
authTokenFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Handler: src/handlers/auth-token.authTokenrHandler
Runtime: nodejs18.x
Architectures:
- x86_64
MemorySize: 128
Timeout: 100
Description: A HTTP GET method to fetch a BASIC auth secret from secrets manager.
Policies:
# Give Permissions to the AuthTokenSecretManager
- AWSSecretsManagerGetSecretValuePolicy:
SecretArn: !Ref AuthTokenSecretManager
Environment:
Variables:
# Make secret manager name accessible as environment variable from function code during execution
SECRET_MANAGER: !Ref AuthTokenSecretManager
Events:
Api:
Type: Api
Properties:
RestApiId:
Ref: ApiGatewayEndpoint
Path: /v1/auth/token
Method: GET
# This is a Lambda function config associated with the source code: add-note.js for adding a note into our SQS Queue
addNotesFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Handler: src/handlers/add-note.addNoteHandler
Runtime: nodejs18.x
Architectures:
- x86_64
MemorySize: 128
Timeout: 100
Description: Includes a HTTP post method to add one note to our SQS Queue.
Policies:
# Give Permissions to the AuthTokenSecretManager and the NotesSQSQueue
- AWSSecretsManagerGetSecretValuePolicy:
SecretArn: !Ref AuthTokenSecretManager
- SQSSendMessagePolicy: # to allow this funciton to send message in queue
QueueName: !GetAtt NotesSQSQueue.QueueName
Environment:
Variables:
# Make secret manager name and queue url accessible as environment variable from function code during execution
SECRET_MANAGER: !Ref AuthTokenSecretManager
QUEUE_URL: !GetAtt NotesSQSQueue.QueueUrl
Events:
Api:
Type: Api
Properties:
RestApiId:
Ref: ApiGatewayEndpoint
Path: /v1/api/note
Method: POST
# This is a Lambda function config associated with the source code: get-all-notes.js for polling our notes from the Queue.
getAllNotesFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Handler: src/handlers/get-all-notes.getAllNotesHandler
Runtime: nodejs18.x
Architectures:
- x86_64
MemorySize: 128
Timeout: 100
Description: Includes a HTTP get method to poll our notes from the Queue.
Policies:
# Give Permissions to the AuthTokenSecretManager and the NotesSQSQueue
- AWSSecretsManagerGetSecretValuePolicy:
SecretArn: !Ref AuthTokenSecretManager
- SQSPollerPolicy: # to allow this funciton to send message in queue
QueueName: !GetAtt NotesSQSQueue.QueueName
Environment:
Variables:
# Make secret manager name and queue url accessible as environment variable from function code during execution
SECRET_MANAGER: !Ref AuthTokenSecretManager
QUEUE_URL: !GetAtt NotesSQSQueue.QueueUrl
Events:
Api:
Type: Api
Properties:
RestApiId:
Ref: ApiGatewayEndpoint
Path: /v1/api/notes
Method: GET
Outputs:
ApiGateway:
Description: "The URL is:"
Value: !Sub "https://${ApiGatewayEndpoint}.execute-api.${AWS::Region}.amazonaws.com/Prod/"
ApiKey:
Description: "You can find your API Key in the AWS console: (Put in the request HEADER as 'x-api-key')"
Value: !Sub "https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/home?region=${AWS::Region}#/api-keys/${ApiGatewayEndpointApiKey}"
Creating the Auth Token
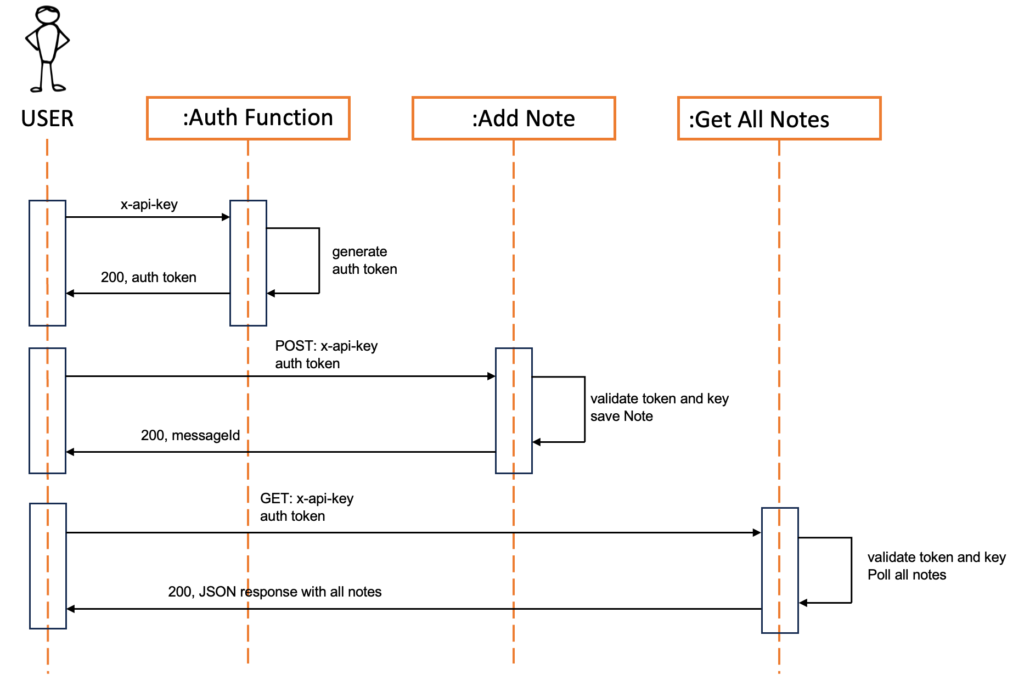
Here we will create a lambda function that when called through an API gateway endpoint, it fetches our credentials .i.e username and password from the AWS Secrets Manager and generates a basic auth credential which is then returned to the user in the API response.
import { GetSecretValueCommand, SecretsManagerClient } from "@aws-sdk/client-secrets-manager";
const clientsecret = new SecretsManagerClient();
// Get the secrets manager name from environment variables
const secretsManagerName = process.env.SECRET_MANAGER;
/**
* A HTTP post method for getting auth token.
*/
export const authTokenrHandler = async (event) => {
if (event.httpMethod !== 'GET') {
throw new Error(`getAuthToken only accepts GET method, you tried: ${event.httpMethod}`);
}
// All log statements are written to CloudWatch
console.info('received:', event);
// Fetch the Auth secret string from AWS Secrets Manager
const secret_value = await clientsecret.send(new GetSecretValueCommand({
SecretId: secretsManagerName,
}));
const auth_token = JSON.parse(secret_value.SecretString);
console.info('Secret-String: ', auth_token);
// Generate basic auth token and return in response data
const username = auth_token.username;
const password = auth_token.authtoken;
const authToken = 'Basic ' + new Buffer(username + ':' + password).toString('base64');
var message = "Successfully authenticated. Use the token below to access other endpoints.";
var status_code = 200;
const responseData = {
message: message,
token: authToken
}
const response = {
statusCode: status_code,
body: JSON.stringify(responseData)
};
// All log statements are written to CloudWatch
console.info(`response from: ${event.path} statusCode: ${response.statusCode} body: ${response.body}`);
return response;
};
Function to add a note in SQS Queue
This function will receive a POST request through the API gateway endpoint with the message/note on the body and authentication credential on the Authorization header. The function will validate the credential and then insert the note into Amazon SQS .
import { GetSecretValueCommand, SecretsManagerClient } from "@aws-sdk/client-secrets-manager";
import { SQSClient, SendMessageCommand } from "@aws-sdk/client-sqs";
const clientsecret = new SecretsManagerClient();
const clientsqs = new SQSClient();
// Get the secrets manager name from environment variables
const secretsManagerName = process.env.SECRET_MANAGER;
// Get the SQS queue URL from environment variables
const sqsQueueURL = process.env.QUEUE_URL
/**
* A HTTP post method to add a message to an SQS Queue.
*/
export const addNoteHandler = async (event) => {
if (event.httpMethod !== 'POST') {
throw new Error(`postMethod only accepts POST method, you tried: ${event.httpMethod} method.`);
}
// All log statements are written to CloudWatch
console.info('received:', event);
// Get token from the authorization header
const authheader = await event.headers.Authorization;
if (!authheader) {
throw new Error(`Authorization token required.`);
}
const auth = new Buffer.from(authheader.split(' ')[1], 'base64').toString().split(':');
const user = auth[0];
const pass = auth[1];
// Get note from the body of the request
const body = JSON.parse(event.body);
const note = body.note;
// Fetch the Auth secret string from AWS Secrets Manager
const secret_value = await clientsecret.send(new GetSecretValueCommand({
SecretId: secretsManagerName,
}));
const auth_token = JSON.parse(secret_value.SecretString);
const username = auth_token.username;
const password = auth_token.authtoken;
// Check if decoded token has same username and password as fetched from secret manager
if ((user != username) || (pass != password)) {
throw new Error(`Authorization credentials invalid. Try again`);
}
const params = {
DelaySeconds: 0,
QueueUrl: sqsQueueURL,
MessageBody: note
};
// Add a message into the SQS queue
try {
const resp = await clientsqs.send(new SendMessageCommand(params));
var items = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(resp));
} catch (err) {
console.log("Error", err);
}
const responseData = {
message: "Note sent to the Queue successfully",
note: {
Message: body.note,
MessageId: items.MessageId,
MD5OfMessageBody: items.MD5OfMessageBody
}
}
const response = {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify(responseData)
};
// All log statements are written to CloudWatch
console.info(`response from: ${event.path} statusCode: ${response.statusCode} message: ${response.message} body: ${response.body}`);
return response;
};
Function to fetch/poll all notes in SQS Queue
This function will fetch/poll all our notes from the SQS queue after receiving a GET request from the API gateway endpoint. The received authorization token will be validated first before sending the notes in the response body.
import { GetSecretValueCommand, SecretsManagerClient } from "@aws-sdk/client-secrets-manager";
import { SQSClient, ReceiveMessageCommand } from "@aws-sdk/client-sqs";
const clientsecret = new SecretsManagerClient();
const clientsqs = new SQSClient();
// Get the secrets manager name from environment variables
const secretsManagerName = process.env.SECRET_MANAGER;
const sqsQueueURL = process.env.QUEUE_URL
/**
* A HTTP get method to get all notes from an SQS Queue.
*/
export const getAllNotesHandler = async (event) => {
if (event.httpMethod !== 'GET') {
throw new Error(`getAllItems only accept GET method, you tried: ${event.httpMethod}`);
}
// All log statements are written to CloudWatch
console.info('received:', event);
// Get token from the authorization header
const authheader = await event.headers.Authorization;
if (!authheader) {
throw new Error(`Authorization token required.`);
}
const auth = new Buffer.from(authheader.split(' ')[1], 'base64').toString().split(':');
const user = auth[0];
const pass = auth[1];
// Fetch the Auth secret string from AWS Secrets Manager
const secret_value = await clientsecret.send(new GetSecretValueCommand({
SecretId: secretsManagerName,
}));
const auth_token = JSON.parse(secret_value.SecretString);
const username = auth_token.username;
const password = auth_token.authtoken;
// Check if decoded token has same username and password as fetched from secret manager
if ((user != username) || (pass != password)) {
throw new Error(`Authorization credentials invalid. Try again`);
}
const params = {
QueueUrl: sqsQueueURL,
MaxNumberOfMessages: 10
};
// Fetch all messages from the queue
try {
const resp = await clientsqs.send(new ReceiveMessageCommand(params));
var items = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(resp));
} catch (err) {
console.log("Error", err);
}
const response = {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify(items)
};
// All log statements are written to CloudWatch
console.info(`response from: ${event.path} statusCode: ${response.statusCode} body: ${response.body}`);
return response;
}
Deployment
Let’s build our application.
$ sam build Build Succeeded Built Artifacts : .aws-sam/build Built Template : .aws-sam/build/template.yaml
Let’s deploy our AWS SAM application
$ sam deploy --guided Configuring SAM deploy ====================== Looking for config file [samconfig.toml] : Not found Setting default arguments for 'sam deploy' ========================================= Stack Name [sam-app]: sam-secrets-management-app AWS Region [us-east-1]: us-east-1 #Shows you resources changes to be deployed and require a 'Y' to initiate deploy Confirm changes before deploy [y/N]: y #SAM needs permission to be able to create roles to connect to the resources in your template Allow SAM CLI IAM role creation [Y/n]: Y #Preserves the state of previously provisioned resources when an operation fails Disable rollback [y/N]: N Save arguments to configuration file [Y/n]: Y SAM configuration file [samconfig.toml]: SAM configuration environment [default]: Previewing CloudFormation changeset before deployment ====================================================== Deploy this changeset? [y/N]: y ---------------------------------------------- CloudFormation outputs from deployed stack ---------------------------------------------- Outputs ---------------------------------------------- Key ApiKey Description You can find your API Key in the AWS console: (Put in the request HEADER as 'x-api-key') Value https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/home?region=us-east-1#/api-keys/na7omt5fj7 Key ApiGateway Description The URL is: Value https://1xws2r3wmb.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/Prod/ ----------------------------------------------- Successfully created/updated stack - sam-secrets-management-app in us-east-1
Testing
Let’s test our deployed application. We start with the token generation endpoint.
# Request
$ curl --header "x-api-key: DipS7ZuqaD84PSN3qnR2r52qurnbriwu5NB8TCpI" https://1xws2r3wmb.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/Prod/v1/auth/token
# Response
{
"message": "Successfully authenticated. Use the token below to access other endpoints.",
"token": "Basic c2FtdXNlcjpXJEU9XzEyUXdOfEhbbW9ZQ0xhXWldPns4RUdoWWctMw=="
} Add a note into Amazon SQS
# Request
$ curl -X POST --header "x-api-key: DipS7ZuqaD84PSN3qnR2r52qurnbriwu5NB8TCpI" --header "Content-Type: application/json" --header "Authorization: Basic c2FtdXNlcjpXJEU9XzEyUXdOfEhbbW9ZQ0xhXWldPns4RUdoWWctMw==" --data '{"note":"My First Note"}' https://1xws2r3wmb.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/Prod/v1/api/note
# Response
{
"message": "Note sent to the Queue successfully",
"note": {
"Message": "My First Note",
"MessageId": "808cdc1f-c3a3-4f8c-a942-2c5e32b30e8a",
"MD5OfMessageBody": "168de9c3732df7b08082699ab613490c"
}
} Poll/fetch notes from Amazon SQS
# Request
$ curl --header "x-api-key: DipS7ZuqaD84PSN3qnR2r52qurnbriwu5NB8TCpI" --header "Authorization: Basic c2FtdXNlcjpXJEU9XzEyUXdOfEhbbW9ZQ0xhXWldPns4RUdoWWctMw==" https://1xws2r3wmb.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/Prod/v1/api/notes
# Response
{
"$metadata": {
"httpStatusCode": 200,
"requestId": "f593b1c6-f551-557e-82c3-ec0bb33f3f3a",
"attempts": 1,
"totalRetryDelay": 0
},
"Messages": [
{
"MessageId": "1ba0e54b-f0a6-4914-9f0a-156005256f4d",
"ReceiptHandle": "AQEBR3hoqeKR15aYqxLp0dITVdtENIx2DtxYA6R+lSrOz453AUtPeC8B2GiHQeCi9Wu6BdtuGz6ONIUiES1dOI9GM3GfL7PwMJqeVtzYUXj+fX4iiuQ0LVs+OrM5Jw9OA+R4TmcAYR/HTgeBY83/2FWYNitZcKNbfi3fnxmX3iFQT4z+OiOFHtsY+Ddjp4x64rEq6PPk/O32zgvIetKPDLgruMynC/2Uk50OQkszlqS/hZLFWeHuKN1W8peqCzrcaeDfPomGeoi1kP75Qfcs0m+2d3/OTSpKkACR+yy0YQ5WNdQldG1yIGIRQC6vrzGoMEzNDAOaqf4MtE307ljnNzVL8TYThTGq36hoktqZo9U5709RcnoL52GYg8gTGN+/L/e2h7Gojnv7tBuImdpyF5bmRg==",
"MD5OfBody": "984bd8254068edc942cb19bff3a78249",
"Body": "My Second Note"
}
]
} All the API call logs are recorded on Amazon CloudWatch.
Clean Up
Remember to clean up after you are done testing the application. Using SAM CLI you can:-
$ sam delete --stack-name sam-secrets-management-app Are you sure you want to delete the stack sam-secrets-management-app in the region us-east-1 ? [y/N]: y Are you sure you want to delete the folder sam-secrets-management-app in S3 which contains the artifacts? [y/N]: y Deleted successfully
In conclusion, as businesses increasingly rely on cloud solutions, the significance of robust credential management becomes apparent, and AWS Secrets Manager as demonstrated emerges as a potent solution. Storing, retrieving and managing secrets on AWS Secrets Manager is evidently easy and multiple AWS SDKs are readily available to support these capabilities within the code. AWS Secrets Manager also easily integrates with other AWS services making it usable in different kind of deployments, be it, serverless or traditional architectures.